INTRO – WORKING OF INSTITUTIONS
Institutions are systems or structures that help the government work properly.
They are like the engine parts of a big machine called government.
Institutions keep our democracy organized, smooth, and trustworthy.
This chapter explains – how one major government decision moves through different institutions — from making it, approving it, to checking it.
It helps us see democracy in action, not just on paper.
OFFICE MEMORANDUM
An Office Memorandum (O.M.) is a formal government document.
It contains orders, instructions, or decisions issued by the Government of India.
It is written in an official format and carries the authority of the Government of India.
The famous office memorandum was issued on 13 August 1990.
*MANDAL COMMISSION
-The Mandal Commission was a government-appointed committee created to find out:
- Which social groups in India were educationally and socially backward
- How the government could support them with fair opportunities
-It is officially known as ‘Second Backward Classes Commission’
–Year of formation: 1979
–Formed by: Prime Minister Morarji Desai
–Chairperson: B.P. Mandal
-After studying thousands of villages, towns, and communities, the Commission concluded:
- A large number of communities in India were socially and educationally backward
- They did not have equal access to education, government jobs, or economic opportunities
- These groups needed special support
-The Mandal Commission recommended the 27% reservation for Socially and Economically Backward Classes (SEBC) in central government jobs and public sector services.
-For almost 10 years, the recommendations were not applied.
-Finally in 1990, Prime Minister V.P. Singh decided to implement 27% reservation for OBCs. This decision was officially announced in the famous Office Memorandum (13 August 1990)
-The reservation decision was challenged in the Supreme Court. This case was known as the ‘Indira Sawhney and others Vs Union of India case’.
–In the Indra Sawhney Case (1992), the Supreme Court:
- Upheld 27% reservation for OBCs
- Introduced the concept of “Creamy Layer” (wealthier OBCs not eligible)
- Fixed a 50% cap on total reservation
This balanced both social justice and merit.
DECISION MAKERS
In a democracy like India, no single person takes decisions alone.
Every major government decision goes through a chain of important people and institutions.
This “team” of decision makers includes:
- Prime Minister (PM) – The PM is the head of government and the most powerful political authority.
- President – is the head of the state and is the highest formal authority in the country.
- Parliament – consists of the President and two Houses, Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha.
NEED FOR POLITICAL INSTITUTIONS
Political institutions are the building blocks of our government. They help the country run in an organized, fair, and efficient way. They are like the engine that drives the whole system of democracy.
There are some reasons on why are political institutions Necessary:
1. To Take Decisions for the Country
Important issues like education, health, defence, budget, and welfare schemes need proper decision-making.
Political institutions help decide what should be done for the nation.
2. To Implement Those Decisions
Decisions become meaningful only when they are put into action.
Institutions like ministries and civil servants implement government policies on the ground.
3. To Resolve Disputes and Maintain Peace
Courts and other institutions settle conflicts between – People, States, and Government bodies. This keeps society calm, fair, and orderly.
4. To Make Democracy Function Smoothly
Democracy needs rules, procedures, and transparency.
Institutions prevent misuse of power and ensure that leaders remain accountable.
5. To Distribute Power Fairly
No single person runs the whole country. Power is divided among – Parliament (law-making), Executive (implementation), and Judiciary (interpretation). This protects freedom and prevents dictatorship.
PARLIAMENT
Parliament is the heart of Indian democracy. It is where laws are made, the government is challenged, and citizens’ opinions are heard. It acts as the bridge between the government and the people.
If India were a machine, Parliament would be the control room.
*Functions of Parliament
Following are the main Functions of Parliament:
1. Law Making
Parliament makes laws on national issues like education, environment, defence, technology, etc.
2. Controlling the Government
Parliament checks whether the government is working properly or not through – Question Hour, Debates, Motions, and No-Confidence Motion.
3. Representing the People
Members speak on behalf of their states and constituencies.
Parliament reflects the voice of India.
4. Approving the Budget
Government cannot spend money without Parliament’s approval.
This keeps expenses transparent and accountable.
5. Discussing National Issues
Inflation, unemployment, safety, defence, floods — Parliament discusses everything that matters to citizens.
*The Two Houses of Parliament
| Basis of Difference | Lok Sabha (House of the People) | Rajya Sabha (Council of States) |
| Meaning | Lower house of Parliament; represents the people of India | Upper house of Parliament; represents the states and union territories |
| Members | Maximum 552 members | Maximum 250 members |
| Election Method | Members are directly elected by the people | Members are indirectly elected by State Legislative Assemblies; some nominated by President |
| Term | 5 years (unless dissolved earlier) | Permanent House; not dissolved. 1/3rd members retire every 2 years |
| Presiding Officer | Speaker of Lok Sabha | Chairman (Vice-President of India) |
| Representation | Represents the population of India | Represents the states of India |
| Powers in Money Matters | Has more power; Money Bill can only be introduced in Lok Sabha | Has limited power; cannot reject a Money Bill, only suggest changes |
| Control over Government | Can remove the government through a No-Confidence Motion | Cannot pass a No-Confidence Motion |
| Age Requirement | Minimum age: 25 years | Minimum age: 30 years |
| Role in Law Making | More powerful; final say in most matters | Cannot overrule Lok Sabha in joint sessions |
| Dissolution | Can be dissolved | Cannot be dissolved (permanent house) |
*Why Lok Sabha Is More Powerful
The following are the points that show how Lok Sabha is more powerful than Rajya Sabha:
1. Lok Sabha Represents the People Directly
Members of Lok Sabha are directly elected by citizens. This makes Lok Sabha the true voice of the people.
Rajya Sabha represents states, not people directly. So in matters related to public interest, Lok Sabha has a stronger role.
2. Lok Sabha Controls the Government
The Council of Ministers (including the Prime Minister) is responsible only to the Lok Sabha.
3. More Power in Money Matters
Money Bills deal with government spending, taxes, budget, etc.
According to the Constitution:
- A Money Bill can be introduced ONLY in Lok Sabha
- Rajya Sabha cannot reject it
- Rajya Sabha can only suggest changes, but Lok Sabha may accept or ignore them
4. Joint Sessions Favor Lok Sabha
If both houses disagree on a law, a joint session is called.
In a joint session, the number of Lok Sabha members is much larger than Rajya Sabha. It will Results that Lok Sabha’s opinion almost always wins.
5. Lok Sabha Can Be Dissolved, Rajya Sabha Cannot
Lok Sabha’s term is 5 years. It keeps Lok Sabha directly answerable to the people, giving it more democratic power.
Rajya Sabha is permanent and cannot be dissolved.
POLITICAL EXECUTIVE
Every country needs people who take decisions and others who implement those decisions.
In India, this decision-making and implementation is done by the Executive.
But the Executive is not just one group — it is divided into two parts:
-Political Executive
-Permanent Executive (Civil Servants)
*Difference Between Political Executive and Permanent Executive
| Basis of Difference | Political Executive | Permanent Executive |
| Who are they? | Elected representatives who run the government | Appointed officials (civil servants/bureaucrats) who assist the government |
| Selection Method | Elected by the people through elections | Selected through exams and recruitment procedures (e.g., UPSC) |
| Duration of Service | Temporary – remain in power only for their term (usually 5 years) | Permanent – work until retirement |
| Decision-Making Power | Have the final decision-making power | Only advise and implement decisions; do not take final decisions |
| Accountability | Accountable to the public and the Parliament | Not directly accountable to the people |
| Change with Elections? | Yes, changes after every election | No, continues even if government changes |
| Expertise | May not be experts in administration | Highly trained and experienced in administration |
| Examples | Prime Minister, Chief Minister, Ministers | IAS officers, IPS officers, IFS officers, other government officials |

*PRIME MINISTER
In a parliamentary democracy like India, the most powerful and central figure in the government is the Prime Minister (PM).
- He/She is the Real Head of the Political Executive.
- The PM is the one who actually runs the country, takes decisions, and guides the nation.
- The President appoints the Prime Minister.
- Usually, the President invites the leader of the party (or group of parties) that has – Maximum seats, and Majority support in Lok Sabha.
- Once elected as the PM, he/she forms the Council of Ministers.
- Powers of the Prime Minister:
- Leader of the Government: He makes decisions on policies, bills and issues.
- Head of the Council of Ministers: The PM chooses all ministers, Distribute work among them, and Can remove a minister if needed.
- Controls the Administration: All major departments work under PM’s supervision.
- Main Spokesperson of the Government: The PM represents the country at national level, in international meetings, and on global platforms
- Link Between President and Cabinet: The PM keeps the President informed about government decisions and updated on important issues
*COUNCIL OF MINISTER
- The Council of Ministers is a group of ministers appointed by the Prime Minister to assist in running the government.
- They help the PM run the government, make decisions, frame policies, and ensure every ministry functions properly.
- Prime minister and Council of minister together form the Political Executive of the country.
- They are responsible for different government departments like education, finance, health, defence, agriculture, etc.
- It usually has 60 to 80 Ministers of different ranks.
- Cabinet Ministers: They are usually toplevel leaders of the ruling party who are in charge of the major ministries.
- Ministers of State with independent charge: They are usually in-charge of smaller Ministries. They participate in the Cabinet meetings only when specially invited.
- Ministers of State: They are attached to and required to assist Cabinet Ministers.
- How they are Appointed?
- The Prime Minister selects the ministers.
- The President appoints them on the PM’s advice.
- Ministers must be members of the Parliament (Lok Sabha or Rajya Sabha).
- If someone is not an MP, they must get elected within 6 months, or they must leave the post.
Powers and Functions of the Council of Ministers:
- Assist the Prime Minister: They help the PM in decision-making and policy formation.
- Head Various Ministries: Each minister is in charge of a specific department
- Implement Laws and Policies: Once Parliament passes a law, the Council of Ministers ensures it is implemented effectively.
- Responsible to the Lok Sabha: They must explain and justify their decisions to the Parliament. If the Lok Sabha loses confidence in them, they must resign.
- Collective Responsibility: All ministers are collectively responsible to the Lok Sabha.
*PRESIDENT
- In a democracy like India, the President is the head of state.
This means that the President is the country’s highest authority, even though he or she does not control the day-to-day operations.
- He/She is the constitutional head of the Indian Union.
- He/She is the supreme commander of the defence forces
- He/She is the first citizen of India
- The President is not elected directly by the people.
- He/she is elected by an Electoral College that includes:
- Elected members of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha
- Elected members of State Legislative Assemblies
- The President holds office for 5 years. And can be re-elected (there is no limit on the number of terms).
- Powers of the President
- Executive Powers: Appoints the Prime Minister, ministers, Governors, judges, ambassadors.
- Legislative Powers: Summons and dissolves Parliament, Signs bills to make them laws.
- Financial Powers: National Budget is presented in the President’s name. Money Bills need President’s approval to be introduced.
- Judicial Powers: Appoints Supreme Court and High Court judges. Can grant pardons or reduce punishments.
- Military Powers: President is the supreme Commander of the Army, Navy, and Air Force. Also he appoints chiefs of all three forces.
- Diplomatic Powers: Signs treaties, sends and receives ambassadors.
THE JUDICIARY
A country needs an authority that protects rights, settles disputes, and ensures everyone obeys the law. This authority is called the Judiciary.
It is the system of courts in India that protects justice and keeps the country running smoothly.
In our democracy, the judiciary acts like a protector of justice, a guardian of the Constitution, and a shield for citizens’ rights. Whenever laws are broken, disputes arise, or someone’s freedom is threatened, the judiciary steps in to ensure fairness, truth, and justice.
The Judiciary is the branch of government that interprets laws, protects fundamental rights, solves disputes, ensures that the government follows the Constitution.
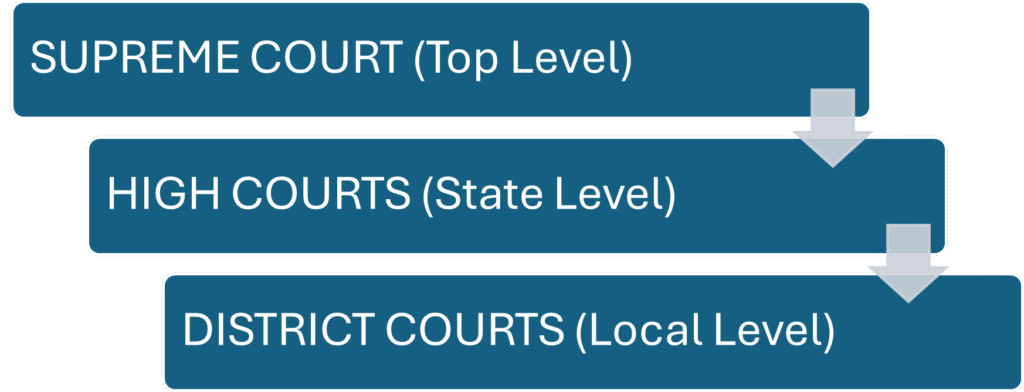
*Structure of Indian Judiciary
*Functions of the Judiciary
1. Dispute Resolution:
The primary work of the judiciary is to resolve disputes.
- Courts settle conflicts between:
- People vs People
- Government vs People
- Government vs Government
- Central Government vs State Governments
- This ensures peace and order in the society.
2. Judicial Review:
The Supreme Court is the final interpreter of the Constitution.
- Courts check whether laws or actions of the government follow the Constitution.
- If something violates the Constitution, the courts can cancel it.
- This protects citizens from misuse of power.
3. Upholding the Law and Enforcing Fundamental Rights
- Judiciary ensures that everyone obeys the law.
- When any Fundamental Right is violated (like equality, freedom, or life), citizens can directly go to the courts.
- Courts can order the government to protect and restore these rights.
4. Interpretation of the Constitution
- The Constitution is the supreme law, but sometimes its meaning needs clarification.
- The judiciary interprets:
- What a law actually means
- How it should be applied
- These interpretations become guiding principles for the country.
5. Providing Justice to All
- Judiciary makes sure that trials are fair, investigations are proper, and nobody is punished without evidence.
- Everyone—rich or poor—gets equal and fair treatment in courts.
- It ensures that the rule of law is followed.
*Independence of Judiciary
The judiciary serves as a shield, protecting our rights. To keep this wall strong, judges must be able to make fair rulings without getting influenced by the government, powerful individuals, or anybody else. This special freedom is known as judicial independence.
Independence of Judiciary’ means courts can make decisions without interference from the Executive (Government) or Legislature (Parliament).
Independence of Judiciary can be seen through:
- Secure Tenure of Judges: Once appointed by the President, judges cannot be removed easily. They can be removed only through a long process called impeachment
- Fixed Process of Appointment: The judges of the Supreme Court and the High Courts are appointed by the President on the advice of the Prime Minister and in consultation with the Chief Justice of the Supreme Court.
- Salary & Allowances Cannot Be Reduced: The government cannot reduce them to influence decisions.
- Judiciary Is Separate from the Executive: Courts work independently and are not controlled by the government.
- Freedom to Decide Cases: Judges can interpret the laws freely.
- The Supreme Court Controls Its Own Work: The higher judiciary can decide – its own rules, which cases to hear, and how to handle court procedures
