INTRO – ENDOCRINE SYSTEM AND ADOLESCENCE
Adolescence is one of the most exciting phases of life. It usually begins around 10–12 years and continues till 18–19 years. During these years, you may notice many things happening at the same time.
The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce hormones — special chemicals that act like tiny messengers. These hormones travel in your blood and tell different parts of your body when to grow, how to develop, and how to feel.
Endocrine system = Glands + Hormones
The Endocrine System is the body’s internal communication network, and adolescence is the time when this network becomes super active.
HORMONES AND ENDOCRINE GLAND
*What Are Glands
Glands are special organs in our body that make and release various chemical substances.
These chemicals help the body grow, stay healthy, digest food, control temperature, and even fight stress.
There are two main types of glands:
- Exocrine Glands
- Endocrine Glands
1. Exocrine Glands – The Ones with Ducts
- Exocrine glands have tubes called ducts to carry the substances they make.
- They release their products at specific places
- They do not produce hormones
- Examples:
- Salivary glands → produce saliva
- Sweat glands → produce sweat
- Sebaceous glands → produce oil on skin
- Tear glands → produce tears
2. Endocrine Glands – The Ductless Ones
- These glands do not have ducts.
- They release their chemical products — called hormones — directly into the bloodstream.
- Release hormones directly into blood.
- Produce hormones
- Hormones control growth, metabolism, emotions, stress, and reproduction
- Examples:
- Pituitary gland
- Thyroid gland
- Adrenal glands
- Pancreas
- Testes (boys)
- Ovaries (girls)
*what are Hormones
Hormones are chemical messengers made by endocrine glands. They travel through blood and control almost every activity in the body.
*Major Endocrine Glands and Their Hormones
1) Pituitary Gland – “The Master Gland”
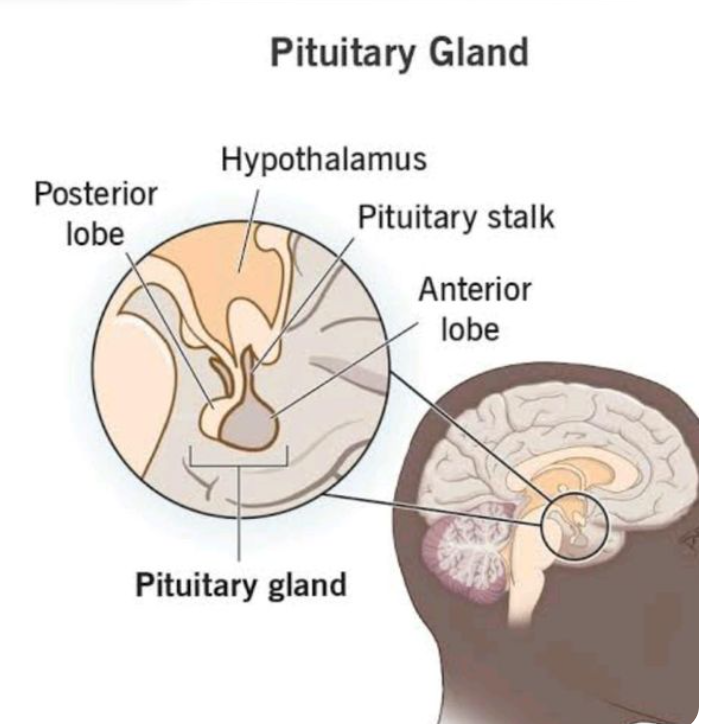
- Located at Base of the brain
- Growth hormone + hormones controlling other glands
- Controls all other endocrine glands
- Helps the body grow taller (via Growth Hormone)
- Produces hormones that regulate thyroid, adrenal glands, and reproductive organs
2) Thyroid Gland – Body’s Energy Manager
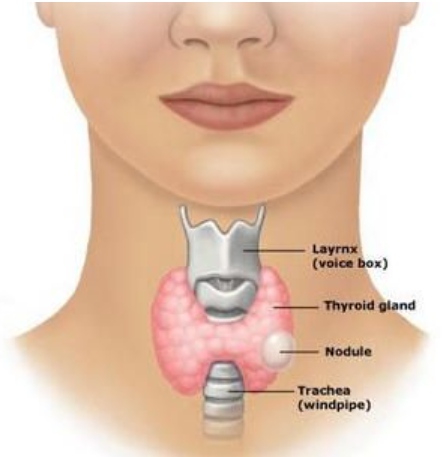
- Located in Neck region
- Hormone name is Thyroxine
- It Controls metabolism (how fast your body uses energy)
- It affects body weight and temperature
- Important for brain development
- Needs iodine to make hormones
3) Adrenal Glands – “Emergency Responders”
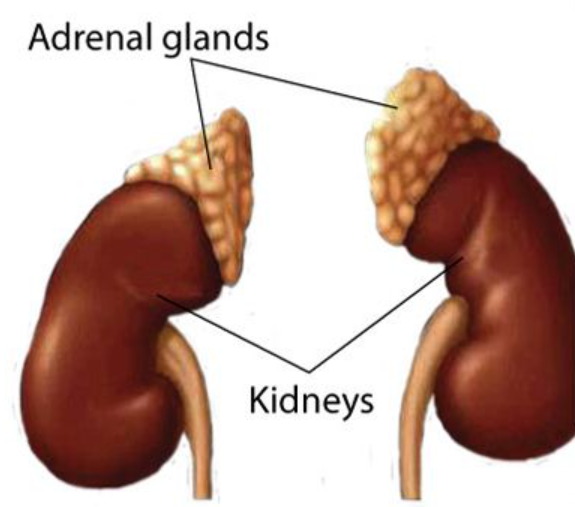
- Located On top of each kidney
- Hormone name is Adrenaline
- Helps the body handle stress and fear
- Increases heartbeat and breathing rate
- Prepares the body for “fight or flight”
4) Pancreas – Blood Sugar Controller
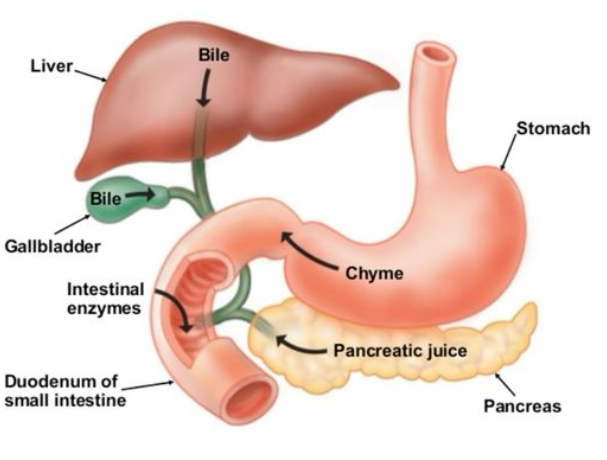
- Located near the stomach
- Hormone name is Insulin
- Maintains blood sugar level
- Prevents too much sugar in blood
- Helps the body use glucose for energy
- Lack of insulin causes diabetes.
5) Reproductive Glands – Puberty Controllers
–Testes (in boys)
- Hormone name is Testosterone
- Growth of beard & deeper voice
- Muscle development
- Sperm production
–Ovaries (in girls)
- Hormones are – Oestrogen & Progesterone
- Breast development
- Menstrual cycle
- Maturation of eggs
PUBERTY
Puberty marks the biological start of adolescence. It is the phase when the body becomes capable of reproduction and starts developing new characteristics.
Girls usually begin puberty between 10–14 years
Boys usually begin puberty between 11–15 years
Hormones play the main role in triggering all changes of puberty.
*The various changes which occur in boys during puberty:
- Increase in Height
- Broadening of Shoulders
- Voice Becomes Deep
- Growth of Hair
- Development of Testes
- Increased Sweat & Oil Glands Activity
- Emotional Changes
*The various changes which occur in girls during puberty:
- Increase in Height
- Breast Development
- Onset of Menstruation
- Growth of Hair
- Development of Ovaries
- Skin & Sweat Changes
- Emotional Changes
*Changes in Reproductive Organs
As puberty begins, the reproductive organs finally mature and become fully functional. This happens due to hormonal changes controlled by the pituitary gland.
– In Boys
- Testes grow fully and start producing sperms.
- The process of sperm formation is called spermatogenesis.
- Sperms are the male gametes, and they have the ability to move (motile).
- The penis also becomes larger and fully developed.
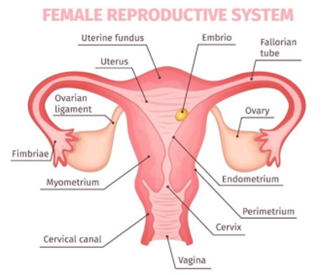
–In Girls
- Ovaries become active and start producing female gametes called ova (eggs).
- This release of an ovum every month is called ovulation.
- One ovary release one egg roughly every 28 days.
- What happens after the ovary releases an egg?
- The uterus prepares itself to receive the egg.
- The uterine lining becomes thick and spongy.
- Blood vessels increase to nourish a possible baby.
*Menstrual Cycle (28-Day Cycle)
If the egg is not fertilized, both the egg and the thick uterine lining are shed from the body. This flow of blood and tissue is called menstruation.
The human menstrual cycle has four phases:
Phase 1: Menstruation (Day 1–4)
- The thick lining breaks.
- Blood, mucus, and the unfertilized egg are expelled.
Phase 2: Follicular Phase (Day 5–12)
- The uterus lining starts rebuilding.
- The lining becomes thick again.
Phase 3: Ovulation (Day 13–14)
- The ovary releases a mature egg.
- This egg moves into the fallopian tube.
Phase 4: Luteal Phase (Day 15–28)
- The uterus lining becomes even thicker.
- It prepares for implantation (in case fertilization happens).
- If pregnancy does NOT happen → lining breaks → menstruation starts again.
#Menarche: First menstrual flow (usually at the start of adolescence).
#Menopause: Menstrual cycle stops permanently (around age 45–50).
*Determination of the Sex of the Baby
Humans have 23 pairs (46 total) chromosomes. Out of these, 22 pairs are normal body chromosomes. The 23rd pair is called the sex chromosomes because they decide whether the baby will be a boy or girl.
Girls have XX chromosomes, while boys have XY chromosomes.
In humans, the mother’s egg always carries only one type of sex chromosome – X. However, the father’s sperms are of two types: some carry X, and some carry Y. This difference plays the main role in deciding the baby’s sex.
X (egg) + X (sperm) = XX → Girl baby
X (egg) + Y (sperm) = XY → Boy baby
Therefore, the sex of the baby depends completely on which sperm reaches the egg first — the X-sperm or the Y-sperm.
This means the father determines the sex of the baby, not the mother.
*Emotional Changes at Puberty
During adolescence, hormones affect not only the body but also the mind.
Common emotional changes:
- Mood swings
- Feeling confused or sensitive
- Sudden anger or sadness
- Attraction towards the opposite sex
- Desire for privacy
- Questioning and exploring personal identity
NUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENTS DURING ADOLESCENCE
Good food is not just fuel—it’s the building block of a strong and confident future.
During adolescence, the body needs:
- More energy for rapid growth
- More nutrients to support bones, muscles, and hormones
- A strong immune system
- A healthy mind for better focus and mood balance
*Essential Nutrients Needed by Adolescents
- Carbohydrates & Proteins – The Energy and Growth Boosters
- Calcium – For Strong Bones & Teeth
- Iron – For Healthy Blood
- Vitamins & Minerals – The Body Protectors
PERSONAL HYGIENE DURING ADOLESCENCE
During Adolescence, the body becomes more prone to sweat, oiliness, skin problems, and infections. That’s why maintaining personal hygiene is extremely important.
Cleanliness during adolescence keeps the body healthy, boosts confidence, and prevents diseases.
*Essential Personal Hygiene Habits During Adolescence
- Regular Bathing
- Wearing Clean Clothes
- Skin Hygiene
- Dental Care
- Nail and Hand Hygiene
- Menstrual Hygiene (For Girls)
- Body Odour Care
- Clean Personal Items
PHYSICAL FITNESS DURING ADOLESCENCE
Physical fitness means the ability of the body to perform daily activities without getting tired easily and with strength, stamina, and flexibility. It keeps both the body and mind strong during the rapid growth of adolescence.
A physically fit adolescent can handle daily tasks effortlessly, think clearly, and stay confident.
*How Adolescents Can Stay Physically Fit
- Exercise Daily
- Eat a Balanced Diet
- Sleep Well
- Stay Hydrated
- Avoid Junk Food
- Play Outdoors
DRUG ABUSE AND AIDS
*Drug Abuse
Drug abuse means misusing harmful substances such as tobacco, alcohol, or other addictive drugs. These substances affect the brain, damage the body, and can create lifelong health problems.
The harmful Effects of Drug Abuse are as follow:
- Weakens the heart and lungs
- Causes liver damage
- Reduces growth and immunity
- Loss of memory and concentration
- Mood swings, anger, depression
- Poor performance in studies
- Serious diseases
- Financial and family problems
- Risk of accidents
*AIDS
AIDS stands for Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome.
It is caused by a virus called HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus). HIV attacks the body’s immune system, making it difficult to fight infections.
A person with AIDS becomes weak and easily gets sick because the body’s defence system is damaged.
HIV spreads through specific ways – Unprotected sexual contact, Sharing infected needles or syringes, Transfusion of infected blood.
It is NOT spread through – Touching, hugging, or shaking hands, Sharing food or water, Mosquito bites, Sitting in the same classroom.
